-

Blood sugar control
- Soluble fiber may help to slow your body's breakdown of carbohydrates and the absorption of sugar, helping with blood sugar control.
-

Heart health
- An inverse association has been found between fiber intake and heart attack, and research shows that those eating a high-fiber diet have a 40 percent lower risk of heart disease.
-

Stroke
- Researchers have found that for every seven-grams more fiber you consume on a daily basis, your stroke risk is decreased by 7 percent.
-

Weight loss and management
-
Fiber supplements have been shown to enhance weight loss among obese people, likely because fiber increases feelings of fullness and slows carbohydrate metabolism.
-

Skin health
- Fiber, particularly psyllium husk, may help move yeast and fungus out of your body, preventing them from being excreted through your skin where they could trigger acne or rashes.
-
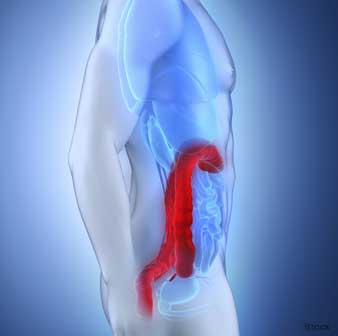
Diverticulitis
- Dietary fiber (especially insoluble) may reduce your risk of diverticulitis – an inflammation of your intestine – by 40 percent.
-
Hemorrhoids
- A high-fiber diet may lower your risk of hemorrhoids by preventing the need for straining.
-

Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Fiber may provide some relief from IBS.
-

Gallstones and kidney stones
- A high-fiber diet may reduce the risk of gallstones and kidney stones, likely because of its ability to help regulate blood sugar.
 Blood sugar control
Blood sugar control Heart health
Heart health Stroke
Stroke Weight loss and management
Weight loss and management Skin health
Skin health Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) Gallstones and kidney stones
Gallstones and kidney stones